New York Braces for Second Highly Contagious Virus Outbreak
Rising Concerns Over Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease Outbreak in the US
New York is facing a growing health challenge as reports of an increase in hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) cases emerge across the eastern United States. This viral illness, known for its high contagiousness, has sparked concern among medical professionals and public health officials.
In addition to the ongoing Legionnaires' outbreak in New York City, which has affected 67 individuals and resulted in three fatalities, doctors in Staten Island are also monitoring a rise in HFMD cases. Similar trends have been reported in several states, including Maryland, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Virginia, Ohio, Kansas, and West Virginia.
Understanding HFMD: Symptoms and Transmission
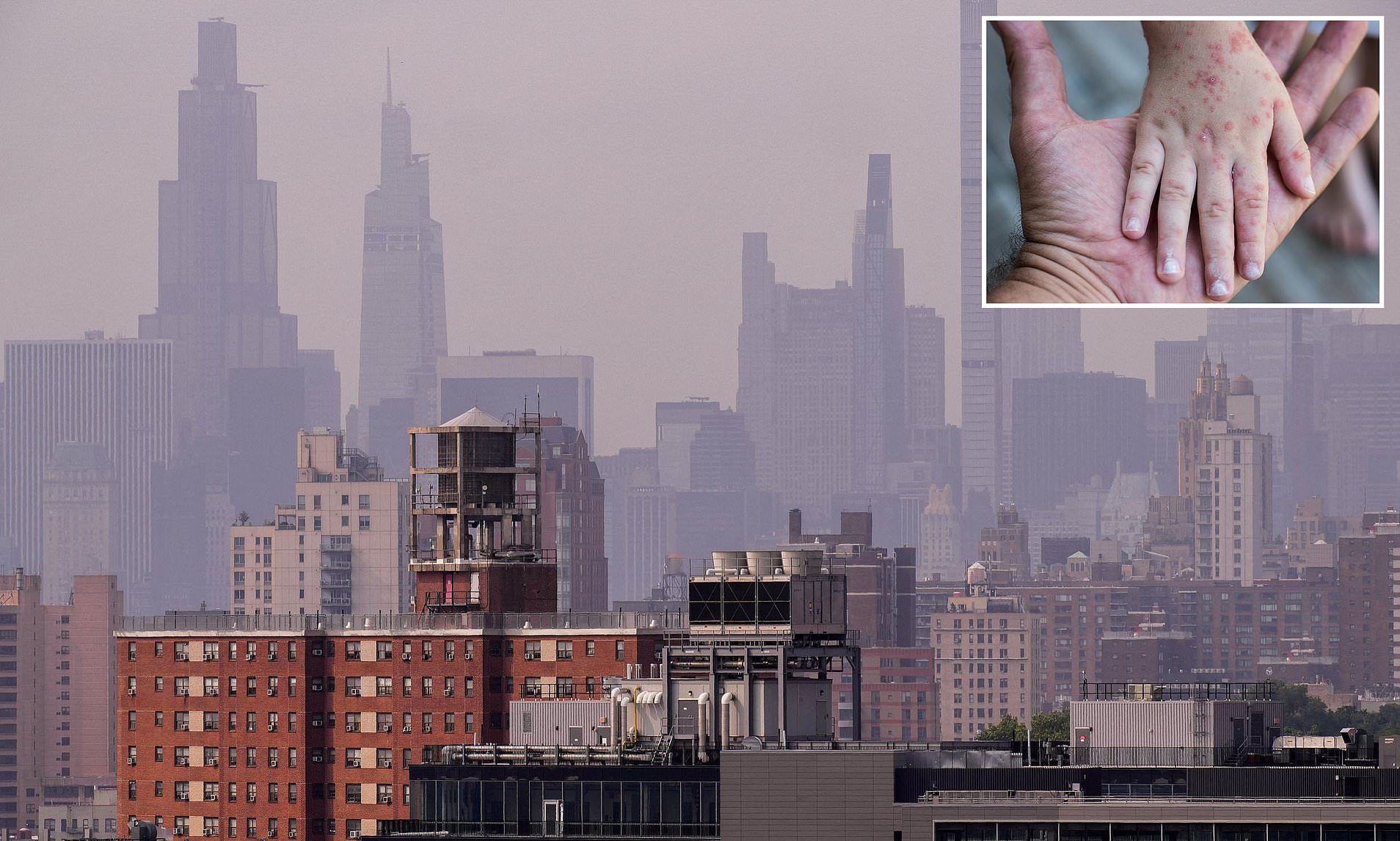
HFMD is caused by the coxsackievirus A16 and typically manifests with painful sores on the hands, feet, and mouth, along with fever and sore throat. The condition primarily affects children under the age of 10, as their immune systems are not yet fully developed. However, adults with weakened immune systems can also be at risk.
Outbreaks often occur in settings where children gather, such as nurseries and schools. The virus spreads easily through direct contact with infected individuals, particularly if they have not washed their hands after using the bathroom. It can also be transmitted through the air or by touching contaminated surfaces.
Seasonal Patterns and Environmental Factors
The disease tends to peak during the summer and early fall months. This is attributed to increased social interactions among children in environments like summer camps, swimming pools, and theme parks. Additionally, warmer and more humid weather conditions may facilitate the survival and spread of the virus.
Dr. Edith Bracho-Sanchez, a pediatrician at Columbia University Irving Medical Center in New York, has observed a significant rise in HFMD cases over the past few weeks—more than she has seen in the last decade. Similarly, Dr. Natasha Burgert, a Kansas-based pediatrician and national spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics, has noted a similar trend nationwide.
Serious Risks and Public Health Measures
While most cases of HFMD resolve within 10 days, the illness can be severe in very young patients. In rare instances, it may lead to complications such as seizures caused by inflammation of the brain’s surrounding fluid.
The virus spreads through contact with bodily fluids from an infected person, including those from blisters, and by consuming contaminated water. Public health experts warn that improperly treated water in water parks can contribute to the spread of the disease. For example, a water park in Philadelphia was temporarily closed in July after a child who visited the facility contracted HFMD.
Prevalence and Management of HFMD
It is estimated that between 10 to 15 million cases of HFMD occur in the United States each year, predominantly among children under five years old. Infected individuals are advised to use over-the-counter pain medications to manage fever and discomfort from mouth sores. Staying hydrated is crucial, as mouth sores can make swallowing difficult and lead to dehydration.
Children diagnosed with HFMD should avoid close contact with others for at least seven days to prevent spreading the infection. Public awareness and preventive measures remain essential in controlling outbreaks and protecting vulnerable populations.

Comments
Post a Comment